目的
了解GraphQL的出现背景并掌握其语法以及apollo server api编写
什么是GraphQl及出现背景?
GraphQL 是一种面向数据的 API 查询风格。
想象一个场景,前端好不容易开发完,产品发现有漏洞,从接口到组件结构都要改,后端不愿意对接口大动干戈,再多写接口给前端想要的数据,前端就要从好几个API里取数据自己组合(当然BFF也可以解决这个问题哦,不过再多写一个BFF层工作量又增加了?emm)
? 所以就有了GraphQL,它是Facebook于 2012 年在内部开发的数据查询语言,在 2015 年开源其的规范,让前端自己描述自己希望的数据形式,服务端则返回前端所描述的数据结构。
GraphQL的特点(如官网所说)
- 请求你所要的数据,不多不少
- 获取多个资源只用一个请求
- 描述所有可能的类型系统(便于维护,根据需求平滑演进,可增加或隐藏字段)
graphQL和restful的对比
Restful,全称Representational State Transfer(表属性状态转移)。定义uri,通过api接口取得资源
Restful:
1. 一个接口只能返回一个资源
2. 用不同的url区分资源
GraphQL:
1. 一个接口能返回多个资源
2. 用不同的类型区分资源
####GraphQL的一些基本概念和语法
类型语言
* 对象类型(自定义)
# Account是一个GraphQl对象类型,name, sex, salery为类型上的字段
type Account {
id: ID!
name: String! # 感叹号表示字段非空
salary(city: cityName = "上海"): Float # 每个字段有0或多个参数,如city,而上海为city的默认参数
}
- 用于查询
# 根据id查用户名
type Query {
employee(id: ID!): Account
}
-
- 变更类型(特殊,自带)
# 用于变更
type Mutation {
createAccount(input: Account): Boolean
}
标量类型:
1. String,Int,Float,Boolean和ID(注:ID代表唯一标识,不能重复),这些参数类型在声明shema时使用
2. [类型]代表数组,如[String]代表字符串数组
####Graphql例子
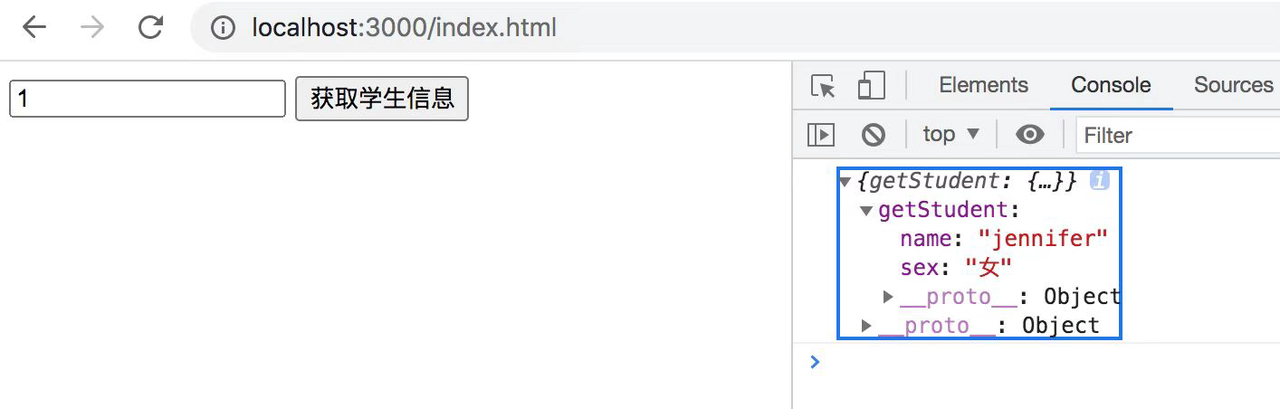
#####一个查找学生,并且在客户端中调用GraphQL的例子
客户端(在public文件夹下?)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" value="" id="input">
<button onclick="getInfo()">获取学生信息</button>
<script>
function getInfo() {
const inputVal = document.getElementById('input').value;
const query = `
query GetStudent(studentId: Int!) {
getStudent(studentId:studentId) {
name
sex
}
}
`;
fetch('/graphql', {
method: "POST",
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Accept': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query,
variables: {
studentId: +inputVal
}
})
}).then(res => res.json())
.then(({ data }) => {
console.log(data);
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
GraphQL结合express编写
const express = require('express');
const { graphqlHTTP } = require('express-graphql');
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// 定义schema,查询和类型
const schema = buildSchema(`
type Student {
studentId: Int
name: String
sex: String
}
type Query {
getStudent(studentId: Int!): Student
}
`);
let students = [{
studentId: 1,
name: 'jennifer',
sex: '女',
}, {
studentId: 2,
name: 'black',
sex: '男',
}];
// 定义查询对应的处理器,schema定义的类型和处理器返回的类型需要一致
const root = {
getStudent({ studentId }) {
return students.find((e) => e.studentId === studentId);
},
};
const app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true, // 开发是否调试
}));
// 用于访问静态资源
app.use(express.static('public'));
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('localhost:3000/graphql'));
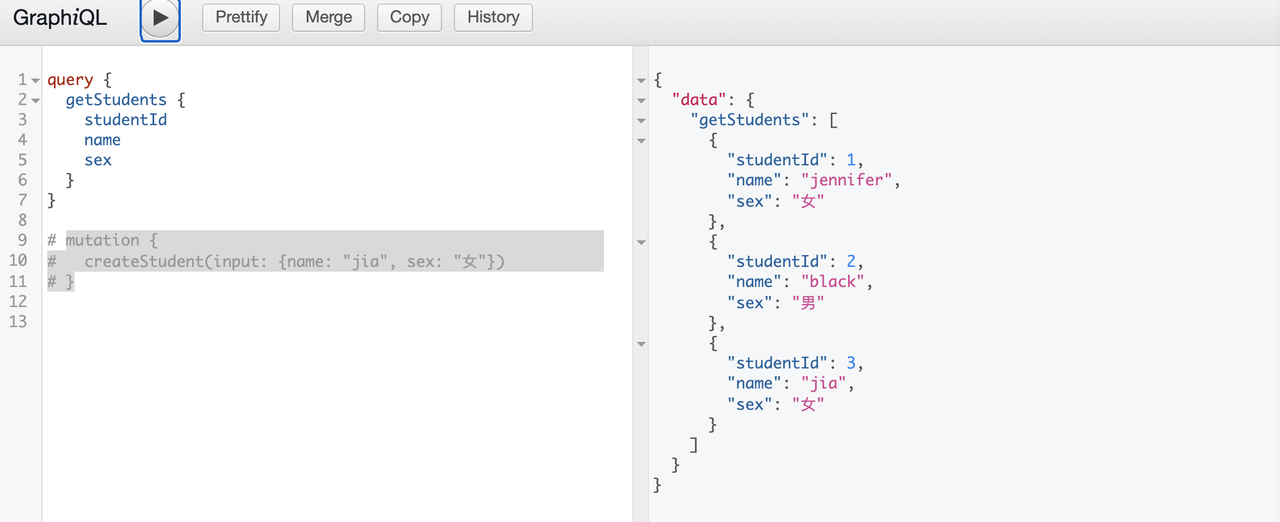
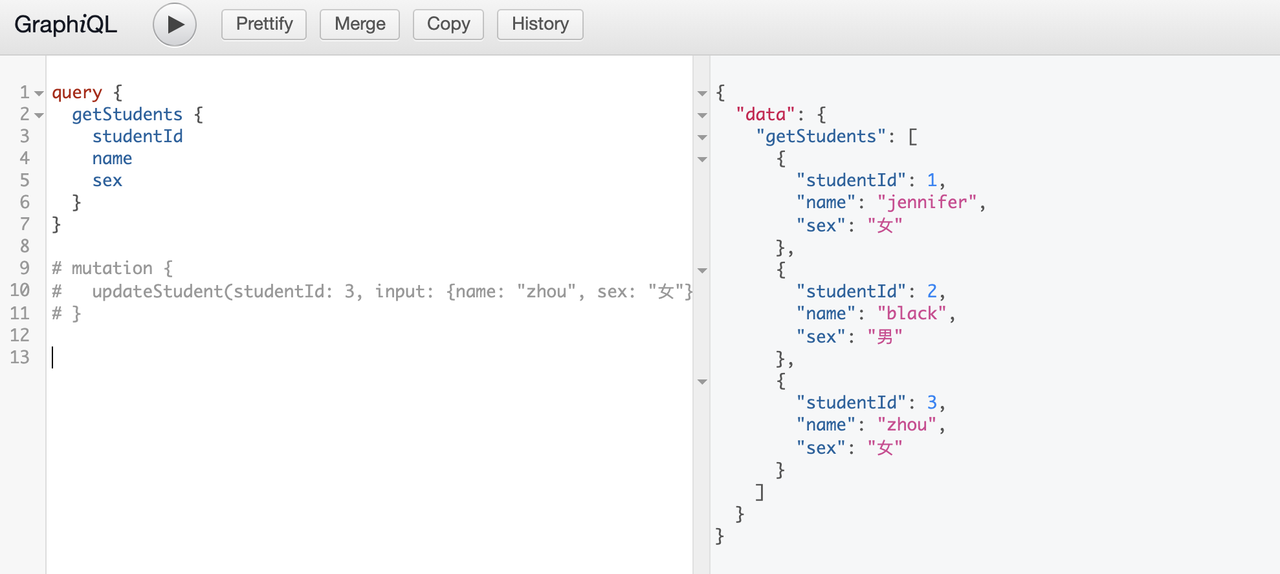
Muataion的练习
在以上例子的基础上。。。
const schema = buildSchema(`
type Student {
studentId: Int
name: String
sex: String
}
input StudentInput {
name: String
sex: String
}
type Query {
getStudents: [Student]
}
type Mutation {
createStudent(input: StudentInput): Boolean
updateStudent(studentId: Int!, input: StudentInput): Boolean
}
`);
let students = [{
studentId: 1,
name: 'jennifer',
sex: '女',
}, {
studentId: 2,
name: 'black',
sex: '男',
}];
const root = {
createStudent({ input }) {
students.push({
studentId: students.length + 1,
...input,
});
return true;
},
updateStudent({ studentId, input }) {
const index = students.findIndex((e) => e.studentId === studentId);
students[index] = {
...students[index],
...input,
};
return true;
},
getStudents() {
return students;
},
};